This document describes the RS232 and USB communication protocols used in some UPS manufactured by Voltronic Power. It started as an “unofficial decoding work” and was later updated with protocol specifications kindly provided by Voltronic Power.
Hardware description
RS232
|
Baud rate
|
2400 bps |
|
Data length
|
8 bits |
|
Stop bit
|
1 bit |
|
Parity
|
none |
|
Cabling
|
9 pins female D-type connector - only 3 wires: TX, RX (crossed) and GND: |
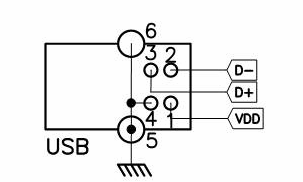
USB
|
Communication
|
Serial over USB with cypress protocol |
|
Cabling
|
|
General
-
All inquiry and control commands and UPS’s replies are terminated by
<cr>. -
Valid inquiry commands will get a reply terminated by
<cr>:-
In a UPS’s reply, unavailable or not supported data is filled with
-. -
In a UPS’s reply, if some data length is less than the definition, there will be enough
#before the data to reach the expected length.
-
-
Accepted control commands are followed by action without any further reply.
-
When invalid control or inquiry commands are sent to the UPS:
-
-
if the command/query starts with
T, the device doesn’t reply anything, -
otherwise the device replies
N<cr>.
-
-
-
the device replies
N<cr>.
-
-
-
the device echoes back the invalid command/query.
-
-
Inquiry commands
By sending inquiry commands you can get the information you need from the UPS.

|
To get a valid reply, all data should be captured at the same time when UPS receives an inquiry command. |
M
|
Query UPS for protocol. Reply
Where
|
P protocol
QS
|
Query UPS for current status and data. Reply
Where:
For example, when PC sends the command And it means:
|
T protocol
QS
|
Query UPS for current status and data. Reply
Where (this note applies):
For example, when PC sends the command And it means:
|
V protocol
QS
|
Query UPS for current status and data. Reply
Where:
For example, when PC sends the command And it means:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
F
|
Query UPS for ratings. Reply
The UPS’s response contains the following information fields:
For example, when PC sends the command And it means:
|
Control commands
By sending control commands you can control the UPS.
T
|
Invoke a 10 seconds battery self-test and then return to utility.
|
S<n>R<m>
|
Shutdown (and restore): shut UPS output off in
|
C
|
Cancel the
|
Q
|
Toggle the UPS beeper.
|
P protocol
CT
|
This command, though supported by devices that implement the P protocol, does nothing.
As a consequence of that, when this command is sent to the UPS, the device doesn’t reply anything (since the command is supported and not invalid, the UPS doesn’t return |
Known problems
The following issues have been reported by some people with ‘V protocol’ devices:
-
S<n>R0000command is known to work as expected (i.e. turn the load off indefinitely) only if mains is present, otherwise, as soon as mains returns the load gets powered. -
After issuing a
S<n>R<m>command, the UPS won’t wait<m>minutes before powering on the load, provided that the following conditions are met:-
if the load has been previously (no matter how long before) powered off through
S<n>R0000command and powered on throughCcommand and -
if AC wasn’t cut after issuing the
S<n>R0000command (i.e. the UPS didn’t turn itself off) and -
if there’s a power outage after issuing the
S<n>R<m>command.
In this case, as soon as mains returns the load gets powered.
-
Revision history
| Rev. | Date | Description | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
1.0 |
01/2014 |
Initial release |
Daniele Pezzini |
2.0 |
11/2015 |
Update the document adding information provided by Voltronic Power |
Daniele Pezzini |